Constellations in the Night Sky
From YoungHerculesWiki
⧼monobook-jumptonavigation⧽⧼monobook-jumptosearch⧽
- Probably part of the "Star Navigation" classes at Cheiron's Academy, the following constellations were mentioned as the cadets were studying for their exams in "1.32 - Cram-Ped".
- More info and pictures To Be Added...
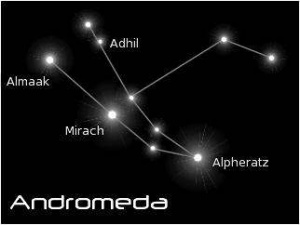
Andromeda
- Mentioned by Lilith.
- Meaning: Daughter of Cassiopeia
- Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. - Wikipedia
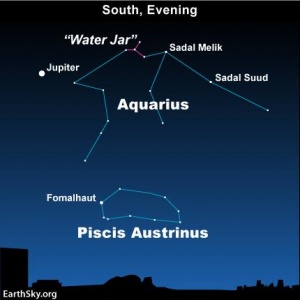
Aquarius
- Mentioned by Pincus.
- Meaning: The Water-Bearer
- Aquarius is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Aquarius is one of the oldest of the recognized constellations along the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. It is found in a region often called the Sea due to its profusion of constellations with watery associations such as Cetus the whale, Pisces the fish, and Eridanus the river. - Wikipedia
Aquila
- Mentioned by Iolaus and Lilith.
- Meaning: The Eagle
- Aquila is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. - Wikipedia
Aries
- Mentioned by Pincus.
- Meaning: The Ram
- Aries is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. - Wikipedia
Auriga
- Mentioned by Lilith.
- Meaning: The Charioteer
- Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. - Wikipedia
Boötes
- Mentioned by Lilith.
- Meaning: The Herdsman
- Boötes is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. - Wikipedia
Camelopardalis
- Mentioned by Lilith.
- Meaning: The Giraffe
- The constellation was introduced in 1612 (or 1613) by Petrus Plancius. Some older astronomy books give an alternative spelling of the name, Camelopardus. First attested in English in 1785, the word camelopardalis comes from Latin, and it is the romanisation of the Greek "καμηλοπάρδαλις" meaning "giraffe", from "κάμηλος" (kamēlos), "camel" + "πάρδαλις" (pardalis), "leopard", due to its having a long neck like a camel and spots like a leopard. - Wikipedia
Cancer
- Mentioned by Pincus.
- Meaning: The Crab
- One of the twelve constellations of the zodiac and one of the 88 modern constellations. - Wikipedia
- The creation of the constellation is explained in Greek mythology by the short-lived association of the crab Karkinos with one of the Twelve Labors of Hercules, in which Hercules battled the multi-headed Lernaean Hydra. Hera had sent Karkinos to distract Hercules and put him at a disadvantage during the battle, but Hercules quickly dispatched the crab by kicking it with such force that it was propelled into the sky. Other accounts had Karkinos grabbing onto Hercules' toe with its claws, but Hercules simply crushed the crab underfoot. Hera, grateful for Karkinos' effort, gave it a place in the sky. Some scholars have suggested that Karkinos was a late addition to the myth of Hercules in order to make the Twelve Labors correspond to the twelve signs of the Zodiac. - Wikipedia
Canes Venatici
- Mentioned by Iolaus.
- Meaning: The Hunting Dogs
Corona Borealis
Cygnus
- Mentioned by Iolaus.
- Meaning: The Swan
Delphinus
- Mentioned by Iolaus.
- Meaning: The Dolphin
Draco
Polaris
Pegasus
Ursa Major
Ursa Minor
- Mentioned by Gregor.
- Meaning: The Little Bear